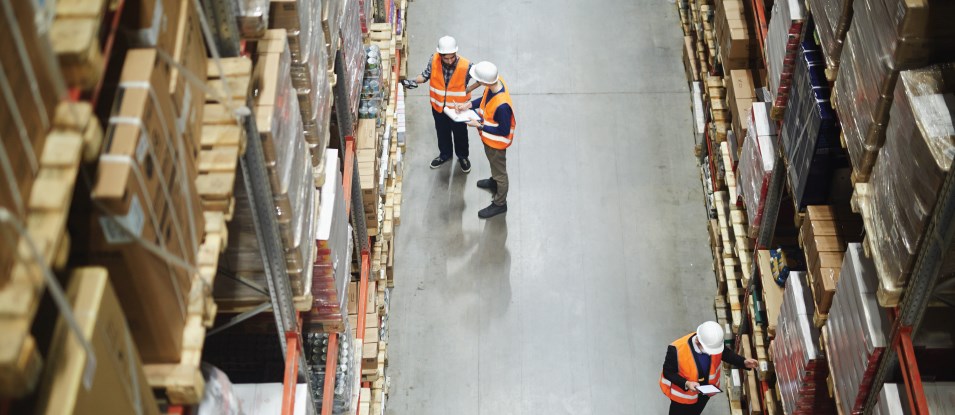
A critical part of any successful company is taking care of all the intricacies of the business through efficient management, planning, and control. These processes together form Logistics Management.
Logistics management tracks your organisation’s workflow, from the procurement of the raw materials to the distribution of the finished goods. The effective storage and movement of goods achieved through logistics management helps organizations reduce expenses and enhance customer services.
Elements of logistics management
Logistics management is a supply chain management component that involves a number of activities, including:
- Inbound and outbound transportation management
- Warehousing
- Materials management
- Selecting appropriate vendors
- Fleet management
- Inventory control
- Order fulfillment
- Supply and demand planning
- Finding effective routes of transportation
- Choosing suitable IT and software resources to handle processes
Why is logistics management important?
Logistics management ensures that there is a plan in place to help the company fulfill the needs of the customers and keep track of the resources needed by the company to produce its products or services.
In this world of fierce competition, small slip-ups can lead to huge setbacks. For example, delivering goods in damaged conditions can lead to both loss of money and dissatisfaction among customers. Ineffective logistics software slows down processes, leading to an increase in expenses and delayed shipments and consequently dissatisfied customers returning or scrapping the products/services.
To avoid such issues and mismanagement, companies must invest in good logistics management practices.
Good logistics management ascertains that products are shipped and delivered in an economical, safe and timely manner, resulting in cost savings for the company and an increase in a satisfied and loyal consumer base.
The primary function of logistics management is to deliver the right product to the right customer at the right time.
Logistics management functions
All levels of planning and execution, whether strategic, operational, or tactical, need logistics management to smoothen out their processes. Some major logistics management functions include customer service, procurement of materials, production planning and scheduling, packaging, and assembly.
Logistics management is not a standalone business function; it integrates logistics activities with other functions like marketing, manufacturing, sales, finance, information technology, and human resources.
Types of logistics management
As mentioned above, logistics management includes a number of activities, but these activities can be divided into four broad types that emphasize different supply chain elements. The types are:
- Supply management and logistics – This involves estimating and planning the materials that would be required, when they would be required and how their storage would be done. Here, the examination of the products can be done that are shipped to the customers and receive additional feedback about the same.
- Distribution and mobility of goods – It involves shipping materials, loading, unloading, and identifying the stock of the commodities that would be shipped. Usage of the materials can be tracked and ensured that the supply is moving from the warehouse to the retail locations selling the products to the consumers.
- Production and logistics management – This involves the cyclic procedure of managing the materials required to manufacture a specific product. Businesses analyze and identify the ideal time to manufacture a product and increase or decrease its production so that they can accurately meet consumer demands.
- Reverse logistics and product return – As the name goes, it is the transportation of products from the end-users to the supply chain. This type involves processes that are carried out after a sale, like when there is a request for return or replacement from the customer for refurbishing, repairing, exchanging, disposal or recycling.
The Logistics Cycle
Let’s take a deeper look at the processes involved in a logistics cycle:
- Serving Customers – Logistics are used to monitor the demand for various products across different geography continuously so the company produces the right quantity of products and serve their customers by providing them with the products they need.
- Product Selection – Selecting the right product impacts the supply chain system directly. Logisticians need to decide which category of products they want to move to different locations so that they can plan the transportation methods, warehousing, and the place of establishment accordingly.
- Quantification – This step is focused on the calculation of the estimate of quantities required for the procurement of the material from the manufacturer or the supplier. It prepares logisticians for an unexpected demand for materials or large orders that they can fulfill either through import or alternative suppliers.
- Inventory Management – Once there is a sufficient supply of the goods required, they are kept in storage until consumers request a purchase. This storage and distribution of commodities is the work of inventory management in the logistics management system.
- Logistics Management Information System – The supply chain majorly depends on the effective communication between the manufacturer, the supplier, the distributor, and the customer. To achieve proper coordination among these entities, make the process smooth, and eliminate errors, companies invest in logistics management software suited to their needs.
Logistics management is not a one-time procedure. To give your business a competitive edge and have an optimized logistics management system, continuous analysis and feedback are necessary. Accepting new ideas and suggestions, learning from mistakes, creating revised strategies, and opting for new tools and software available are all important to improve the process.